What is an Expert System?
An expert system is a computer program future to solve complex problems and provide the ability to make decisions like a human expert. It does this by extracting knowledge from its knowledge base using the rules of reasoning and inference according to user requests.
The expert system is part of AI, and the first ES develop in 1970, which was the first successful approach to artificial intelligence. As an expert, you solve the most complex problem by extracting the knowledge stored in your knowledge base. The system helps in decision-making for complex problems using both facts and heuristics like a human expert. It is so named because it contains the specialized knowledge of a specific area and can solve any complex problem in that particular area—these systems design for a specific field, such as medicine, science, etc.
The performance of an expert system base on the expert’s knowledge store in its knowledge base. The more ability that store in the knowledge base, the more this system recovers its performance. One of the shared examples of an ES is a suggestion of spelling mistakes when typing in the Google search box.
Examples of Expert System
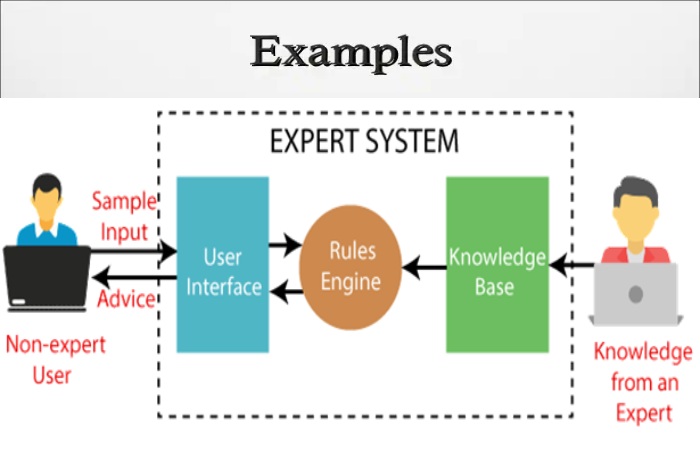
Here are some famous examples of the expert system:
DENDRAL: It was an artificial intelligence scheme that design as an expert chemical analysis system. It has been used in organic chemistry to detect unknown organic molecules using its knowledge base of mass spectra and chemistry.
MYCIN: It was one of the first expert backhaul systems designed to find bacteria that cause infections such as bacteremia and meningitis. It also uses for the recommendation of antibiotics and the diagnosis of blood clotting diseases.
PXDES: It is an expert system used to determine the type and level of lung cancer. To determine the disease, take a photo of the upper body, which looks like a shadow. This gumshoe identifies the type and degree of damage.
CaDeT: The CaDet Expert System is a diagnostic aid system that allows cancer to be detected early.
Features of Expert System
High performance: The expert system delivers high performance to solve any complex problem of a specific area with high efficiency and precision.
Understandable: Response in a way that the user can easily understand. You can receive input in human language and provide results in the same way.
Reliable: It is very loyal to generate an efficient and accurate output.
Very responsive: ES provides the result of any complex query in no time.
Components of An Expert System
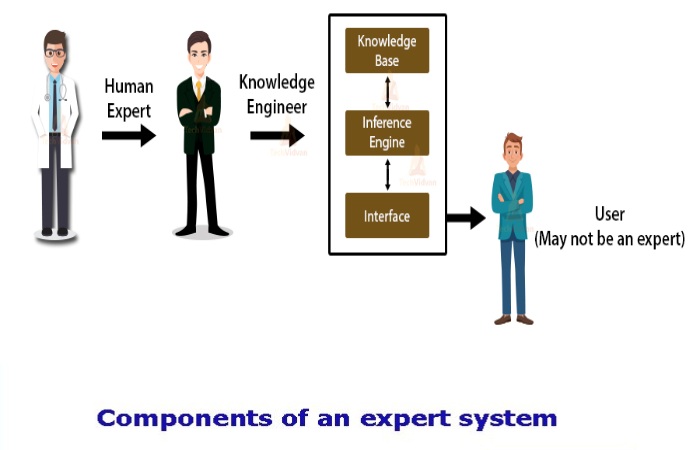
An expert system consists mainly of three elements:
- User interface
- Inference machine
- Knowledge Base
1. User Interface
The expert system interacts with the user through a user interface, takes the input requests in a readable format, and passes them to the inference engine. After getting the reply from the inference engine, it shows the output to the user. In other words, it is a border that helps a non-expert user to connect with the expert system to find a solution.
2. Inference Engine (Engine Rules)
The inference engine is known as the intelligence of the expert system because it is the central processing unit of the system. Apply inference rules to the knowledge base to draw a conclusion or infer new information. It helps to derive an error-free solution to the queries raised by the user.
Using an inference engine, the system extracts knowledge from the knowledge base. There are two types of inference engines:
Deterministic Inference Engine: The deductions drawn from this type of inference engine are assumed to be true. It bases on facts and rules.
Probabilistic Inference Engine: This inference engine covers uncertainty in the conclusions and base on probability.
The inference engine uses the following modes to derive the solutions:
Forward Chaining: Start with the known facts and rules and apply inference rules to add your conclusion to the known facts.
Backward Chaining: This is a backward reasoning method that starts from the target and works backward to prove known facts.
3. Knowledge Base
The knowledge base is a type of storage that stores the knowledge acquired from different experts in a particular field. It is considered an excellent repository of knowledge. The larger the knowledge base, the more accurate the expert system.
It is similar to a database that covers information and rules for a particular domain or topic. The knowledge base can also view in the form of collections of objects and their attributes. As a lion is a thing and its qualities are a mammal, it is not a domestic animal.
Knowledge Base Components
Factual Knowledge: Knowledge-based on facts and accepted by knowledge engineers includes solid understanding.
Heuristic Knowledge: This knowledge base on practice, the ability to guess, evaluation and experience.
Knowledge Representation: It is used to formalize the knowledge stored in the knowledge base using If-else rules.
Knowledge Acquisition: it is the process of extracting, organizing, and structuring the knowledge of the field, specifying the rules that allow acquiring the knowledge of various experts and storing this knowledge in the knowledge base.
Development of an Expert System
Here we will explain how an expert system works by taking an example from MYCIN ES. Here are some steps to create an MYCIN:
- First, the EE must fuel by specialized knowledge. In MYCIN, human experts in the medical field of bacterial infections provide information on the causes, symptoms, and other experts in this area.
- The MYCIN knowledge base successfully update. To test him, the doctor presents him with a new problem. The problem is identifying the presence of the bacteria by entering the details of the patient, including symptoms, current condition, and medical history.
- The ES will need a survey to complete by the patient to know general information about the patient, such as sex, age, etc.
- Now that the system collects all the information, you will find the solution to the problem by applying if-then rules using the inference engine and using the facts stored in the knowledge base.
- In the end, you will provide an answer to the patient through the user interface.
Participants in the Development of the Expert System.
There are three main participants in building the expert system:
Expert: The success of an EE is highly dependent on the knowledge provided by human experts. These experts are the people specialized in that specific field.
Knowledge Engineer: The knowledge engineer is the person who gathers the knowledge of the experts in the field, then encodes this knowledge into the system according to formalism.
End-User: It is a specific person or a group of people who may not be experts, and working in the expert system needs the solution or advice for their complex queries.
Characteristics of Expert System
These are some of the characteristics of an expert system:
Advisor: And also, it is capable of advising the human being for the consultation of any particular ES domain.
Provide Decision-Making Skills: Provides decision-making ability in any field, such as making financial decisions, decisions in medical sciences, etc.
Demonstrate a Device: You can demonstrate any new product, such as its features, specifications, how to use this product, etc.
Problem-Solving: You can solve problems.
Explain a Problem: You are also able to provide a detailed description of an input problem.
Input Interpretation: And also, it can interpret the input given by the user.
Outcome Prediction: It can use to predict an outcome.
Diagnosis: An EE designed for the medical field can diagnose a disease without using multiple components because it already contains several integrated medical tools.
Advantages of the Expert System
- These systems are highly reproducible.
- They can use for places of risk where the human presence is not safe.
- The chances of error are less if the knowledge base contains the correct knowledge.
- And also, the performance of these systems remains stable because they are not affected by emotions, tension, or fatigue.
- They provide a very high speed to reply to a particular query.
Limitations of the Expert System
- The answer from the expert system may be incorrect if the knowledge base contains erroneous information.
- As a human being, you cannot produce creative production for different scenarios.
- And also, its maintenance and growth costs are very high.
- Acquiring knowledge for conception is much more difficult.
- For each domain, we need a specific operating system, which is one of the significant limitations.
- And also, it cannot learn on its own and therefore requires manual updates.
Applications of Expert System
In the field of design and manufacture: It can widely use to design and manufacture physical devices such as camera lenses and cars.
In the area of knowledge: These systems mainly use to publish knowledge relevant to users. The two popular ESs used for this area are an advisor and a tax advisor.
In the financial field: In the financial industries, it uses to detect any possible fraud, suspicious activity and to indicate to bankers whether or not to grant business loans.
In diagnosing and troubleshooting devices: In medical diagnostics, the ES system use, and this was the first area in which these systems operate.
Planning and scheduling: And also, expert systems can also plan and schedule specific particular tasks to achieve that task.
Also Read: What are the Best Big Data Courses for Getting a Job?







